v5 (LATEST)
Devnet
Testnet
Mainnet
Secure Message Transmission Process Using ISO 20022
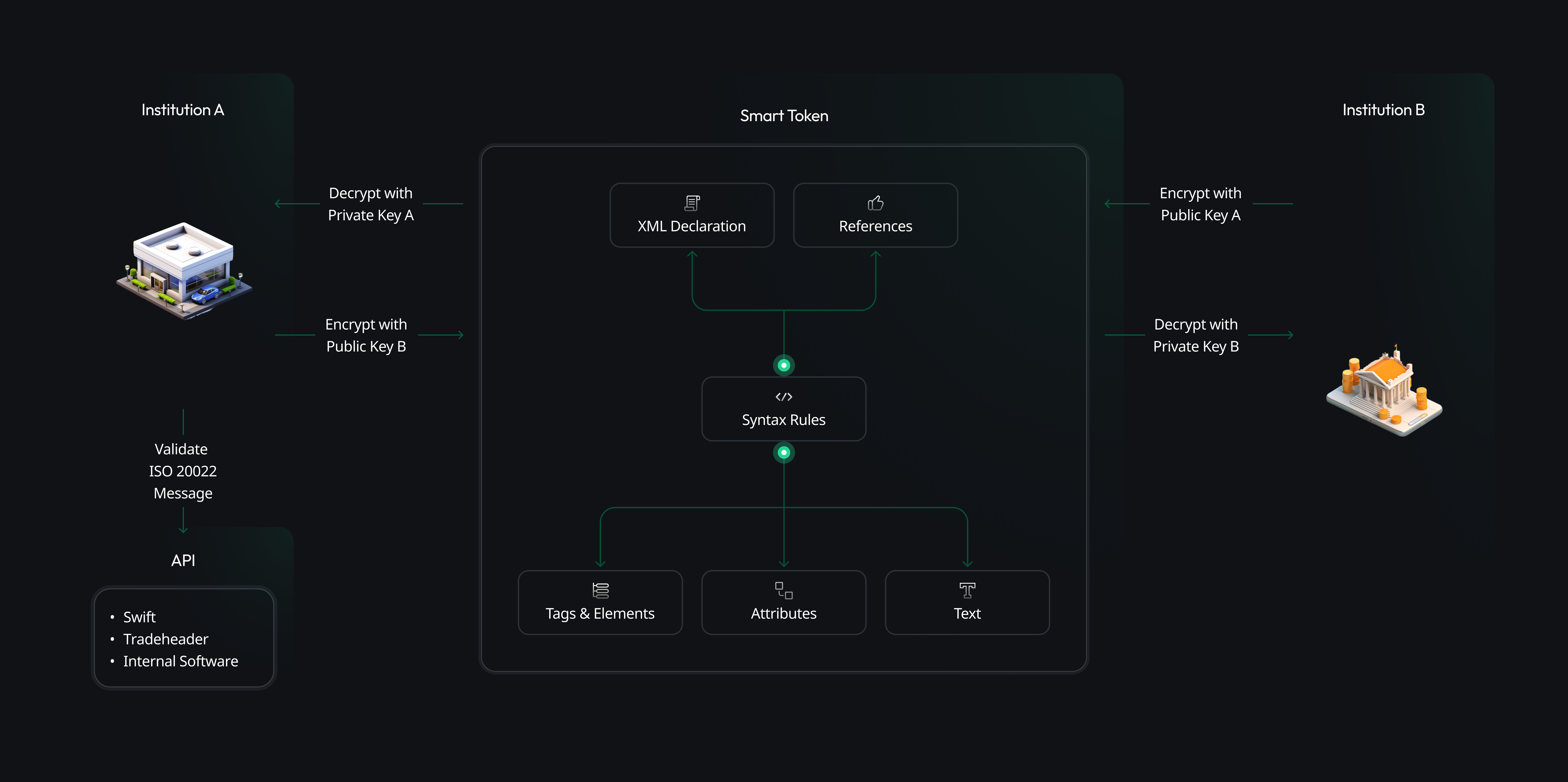
Step-by-Step Explanation
1. Initiation by Institution A
Institution A, which could be a bank or another financial entity, initiates the process of sending a secure message, such as a payment instruction.
2. Validate ISO 20022 Message
Institution A validates the message against the ISO 20022 standard, a messaging standard that enables the electronic exchange of information in the financial industry.
3. Encryption with Public Key B
The validated message is encrypted using the public key of Institution B. This ensures that only Institution B, which possesses the corresponding private key, can decrypt the message.
4. Smart Tokenization
The message is tokenized into a Smart Token, turning sensitive data into a non-sensitive equivalent, known as a "token," that has no meaningful value outside its context.
5. XML Declaration
The structure of the message is based on XML (eXtensible Markup Language), commonly used for sharing data across systems.
6. References and Syntax Rules
The message includes references to previous transactions or relevant documents and adheres to specific syntax rules for proper structure and comprehension.
7. Tags, Elements, and Attributes
Within the XML:
- Tags & Elements: Define and organize the information hierarchically.
- Attributes: Provide additional details about the elements.
8. Text Content
This section contains the actual data within the XML elements.
9. Receipt by Institution B
Institution B receives and decrypts the message using its private key.
10. Encrypt with Public Key A
If Institution B needs to send a response or further information back to Institution A, it will encrypt this data with Institution A's public key.
11. Decryption by Institution A
Institution A then uses its private key to decrypt the message from Institution B.